What is CVE-2025-29927?
A critical improper authorization vulnerability (CVSS 9.1) in Next.js, tracked as CVE-2025-29927, was publicly disclosed on March 21, 2025. Next.js is a popular React-based web framework used for building full-stack applications.
This vulnerability impacts applications that utilize middleware for authorization checks. Middleware functions used to implement access control, session validation, redirects, or security headers on incoming HTTP requests. Unfortunately, this vulnerability allows attackers to slip past these critical security checks and this vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers to circumvent these protections by sending a specially crafted x-middleware-subrequest header.
Next.js utilizes the x-middleware-subrequest header internally to prevent infinite loops that can be caused by recursive requests. The vulnerability exploits process to skip critical checks. Successful exploitation could lead to unauthorized access to restricted pages or APIs, depending on how the application is structured. This technique, despite its simplicity, is quite powerful and allows threat actors to perform unauthorized actions and gain access to protected routes.
What assets are affected by CVE-2025-29927?
This vulnerability affects Next.js versions
- Next.js 11: 11.1.5 through 12.3.4
- Next.js 13: 13.0.0 through 13.5.8
- Next.js 14: 14.0.1 through 14.2.24
- Next.js 15: 15.0.1 through 15.2.2
While all of the above versions are vulnerable, the mechanics of the exploit differ slightly between legacy versions(pre-12.2) and modern versions (12.2 and later versions). Legacy versions are vulnerable when the header is set to
x-middleware-subrequest: pages/_middleware, while modern setups are exploited using repetitive patterns like x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware… or src/middleware:… if using a source directory structure).
This vulnerability only affects self-hosted Next.js applications using Middleware for authentication or security checks that are not validated later in the application.
Applications hosted on Vercel, Netlify, and applications deployed as static exports (that do not execute Middleware) are not affected by CVE-2025-29927.
Are fixes available?
The vendor recommends upgrading to Next.js version 15.2.3.
- For Next.js 15.x, this issue is fixed in 15.2.3
- For Next.js 14.x, this issue is fixed in 14.2.25
- For Next.js 13.x, this issue is fixed in 13.5.9
- For Next.js 12.x, this issue is fixed in 12.3.5
- For Next.js 11.x, this issue is fixed in 12.3.5
Backported patches are also available. Next.js also identified self-hosted Next.js deployments using next start and output: 'standalone' as the highest priority for patching and upgrading.
Are there any other recommended actions to take?
If patching to a secure version is not possible, it is advised to block external user requests that include the x-middleware-subrequest header from reaching your Next.js application. Applications that use Cloudflare can enable a managed WAF rule to do this.
Next.js also recommends validating that your applications do not rely solely on middleware to handle critical authentication and authorization logic.
Is CVE-2025-29927 being actively exploited?
As of March 27th, 2025, there are no reports of this vulnerability being actively exploited in the wild. However, Next.jw is widely used, with over 10 million downloads weekly.
How is CyCognito helping customers identify assets vulnerable to CVE-2025-29927?
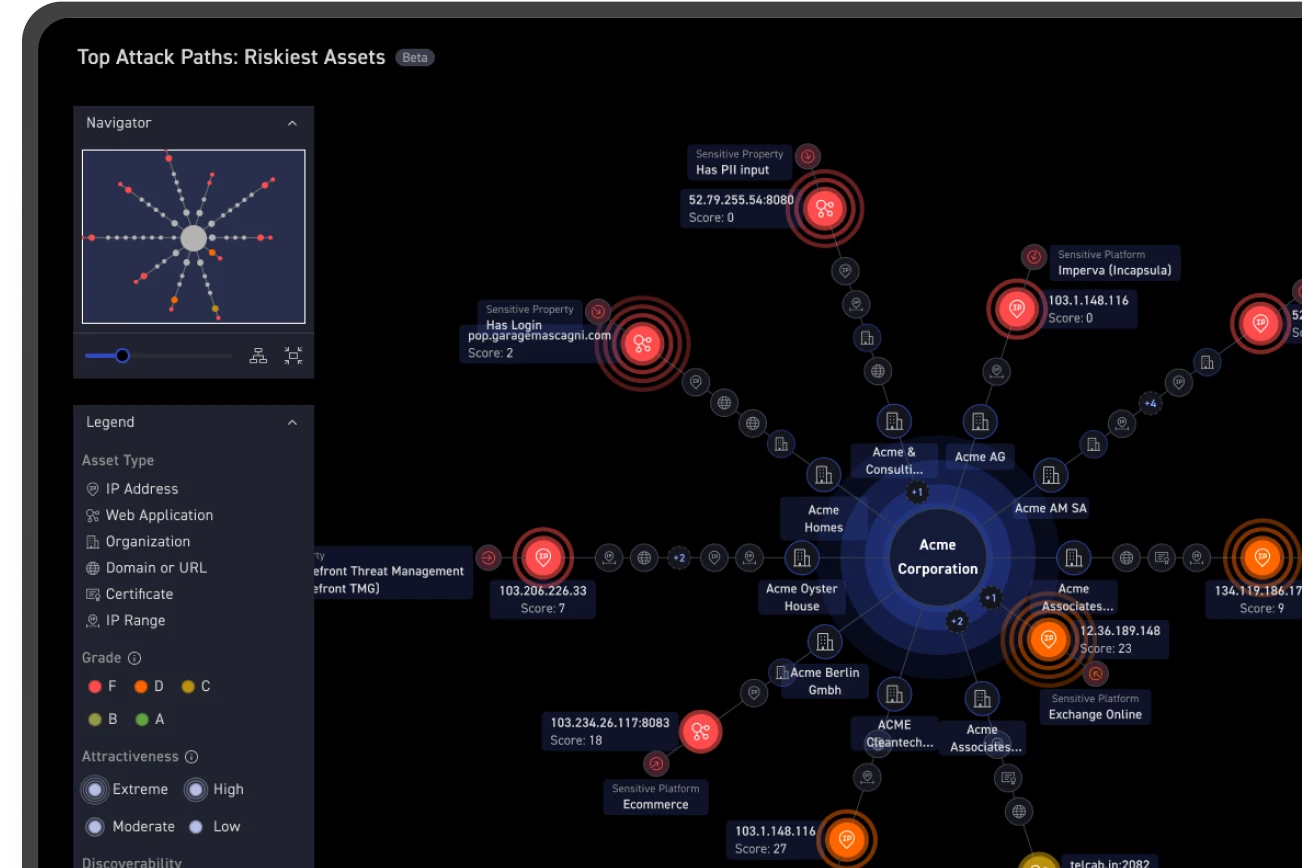
CyCognito published an emerging threat advisory within the CyCognito platform on March 27th and is researching detection capabilities for this vulnerability. CyCognito advises customers to check assets running next.js services to evaluate their exposure, even if they are not explicitly identified as running vulnerable versions.

Figure 1: The alert sent by CyCognito for CVE-2025-29927
Check out CyCognito’s Emerging Threats page for more information on potentially relevant vulnerabilities.
How can CyCognito help your organization?
CyCognito is an exposure management platform that reduces risk by discovering, testing and prioritizing security issues. The platform scans billions of websites, cloud applications and APIs and uses advanced AI to identify the most critical risks and guide remediation. Emerging companies, government agencies and Fortune 500 organizations rely on CyCognito to secure and protect from growing threats. Want to see how it works? Check out our website and explore our platform with a self-guided, interactive dashboard product tour. To learn how CyCognito can help you understand your external attack surface and exposed risks, please visit our Contact Us page to schedule a demo.